MARKET UPDATE - 2022 Q3
MARKET TRENDS - U.S. ECONOMY OUTLOOK
The US economy grew at an annual rate of 2.6 percent in the third quarter, marking its first increase in 2022 and a sharp turnaround after six months of contraction. The report on the gross domestic product, released Thursday by the Bureau of Economic Analysis, revealed a more upbeat snapshot of the economy less than two weeks before the midterm elections, even as high inflation has proved a persistent problem for the US economy.
Even though US consumers bought fewer goods, they continued to spend on healthcare, which helped increase the overall GDP. An increase in government spending at the federal, state, and local levels also contributed to the gains as well. However, the biggest boost came from a narrowing trade deficit, with American retailers importing fewer items and exporting more goods as well as services, such as travel. Trade-related benefits are likely to be short-lived. Economists widely expect GDP growth to slow in the coming months as consumers and businesses continue pulling back in the face of rising interest rates and uncertainty. By next year, many are forecasting a more protracted slump and perhaps even a recession.
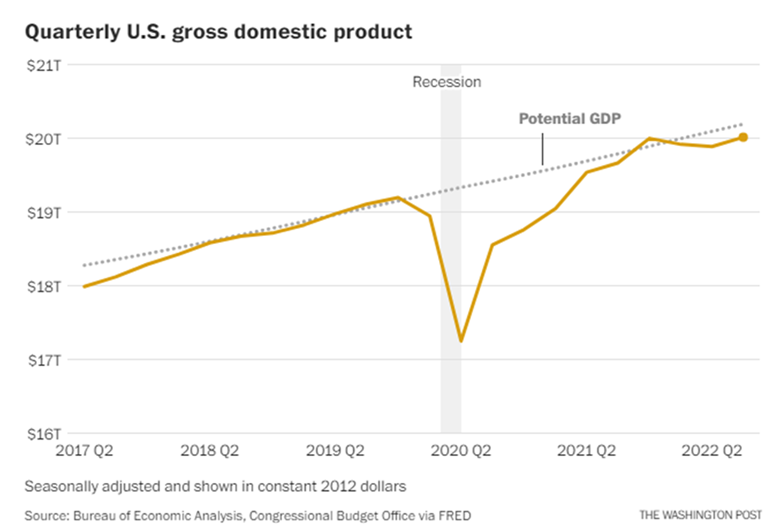
Several recent indicators point to a broader cooling of the economy, most notably in the housing market. Home sales have declined for eight straight months and are likely to keep falling because of rising interest rates. Currently, average mortgage rates for 30-year loans exceeded 7 percent for the first time since the early 2000s.
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis, Congressional Budget Office via FRED, Washington Post
INTEREST RATES & INFLATION IN THE U.S.
The Federal Reserve raised the target range for the federal funds rate by 75bps to 3.75%-4% during its November 2022 meeting. This increase marks the sixth consecutive rate hike and the fourth straight three-quarter point increase, pushing borrowing costs to a new high since 2008. The decision came in line with market forecasts. Policymakers also said that ongoing increases in the target range will be appropriate and that they will take into account the cumulative tightening of monetary policy, the lags with which monetary policy affects economic activity and inflation, and economic and financial developments when deciding on the size of further increases. The message could signal a smaller rate hike in December but during the press conference Chair Powell also noted the ultimate level of interest rates will be higher than previously expected. The Fed aims to attain a stance of monetary policy that is sufficiently restrictive to return inflation to 2%, which remains elevated around 40-year highs
Source: Federal Reserve
HEALTHCARE OVERVIEW IN THE U.S.
The Baby Boomer population continues to age into retirement, which in turn gains them access to Medicare benefits. As a result, a projected 2 million new people will enroll in Medicare annually through 2028. With this increased Medicaid enrollment, government-sponsored healthcare coverage will grow by a projected 19% through 2028. Rising enrollment in Medicare Advantage plans is a key component to controlling increased costs from an aging population. In 2022, 48% of those eligible for Medicare were enrolled in a Medicare Advantage plan, and this is expected to continue to increase. Under a Medicare Advantage plan, the government pays a fixed fee per enrollee to the insurer, who is then financially motivated to improve health outcomes to reduce costs. There have been efforts made by the government to control costs and continue to drive a shift in reimbursement within the industry toward outpatient care. Research has discovered that outpatient facilities are less expensive to develop and operate. However, health systems must reduce or repurpose stranded, higher-cost inpatient space to meet their required returns.
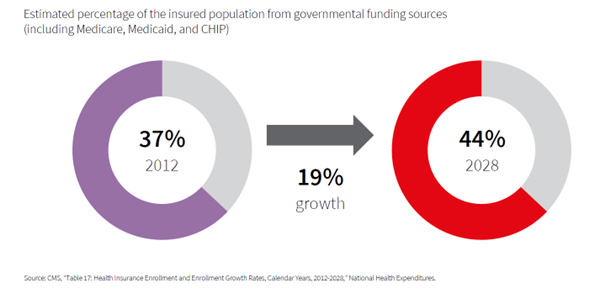
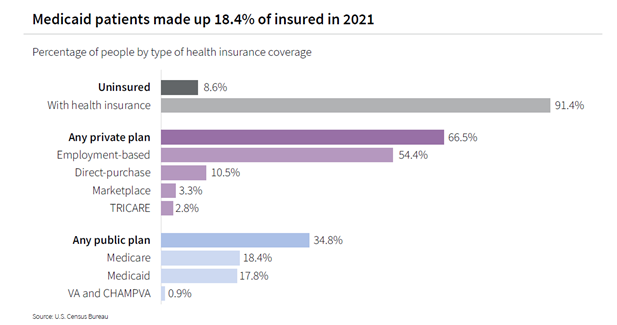
Enrollment in Medicaid increased at the onset of the pandemic and has remained at a high level. This increase is primarily due to government programs that were introduced and then extended. There were 18.2 million (25.6%) more people enrolled in Medicaid in June 2022 than in February 2020, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF). Medicaid rates are predetermined and generally fall well below Medicare rates, which are well below commercial insurance rates. While other factors affect how much healthcare systems ultimately get paid, a higher number of Medicaid and Medicare patients on average will decrease margins.
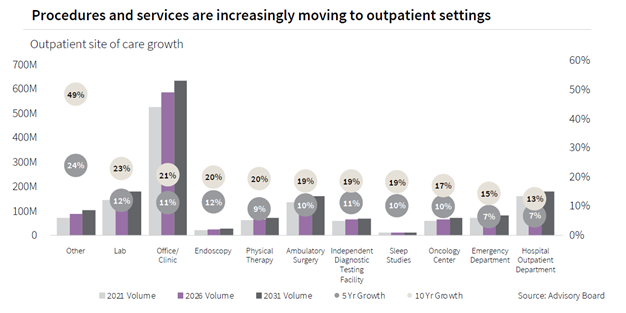
Research has shown that healthcare in The US is shifting away from inpatient facilities to outpatient facilities. As of September 2022, year over- year outpatient revenues grew 30% since 2020 according to Kaufman Hall, while inpatient revenues only grew 8.5% at the same time. Over time, surgical operations have become less invasive and more efficient. As consumers seek more convenient and accessible care, outpatient facilities will ultimately drive provider demand. This shifting healthcare environment will continue to be supported by reimbursement policies, and specialized care options will further drive competition within the industry.
Source: Jones Lang LaSalle Market Research
CONCLUSION
While no commercial real estate sector is immune to the impact of high inflation, a slowing economy, and rising operating costs, the medical office sector is believed to be well-positioned to handle what the foreseeable future has in store. Underlying business fundamentals for medical tenants are stronger than a typical office user, which in turn reduces concern over future income streams.
There is greater stability in demand for medical services and, potentially, spent-up demand from procedures canceled or postponed during the pandemic. In addition, U.S. Census data estimates that one in five Americans will be 65 or older by 2030, rising to one in four by 2060, thereby underpinning demand for medical office facilities.
These fundamentals, along with a limited pool of available medical office assets, should continue to push healthy sales volume. However, pricing expectations of medical office real estate between buyer and seller may widen, particularly for leveraged acquisitions.
